How to Draw Muscles: A Guide to Mastering Human Anatomy
Would you like to know how to draw muscles easily and accurately? This guide breaks down the fundamentals of drawing the major muscle groups of the human body—including the torso, arms, and legs. Understanding the anatomy beneath the skin helps create dynamic poses and realistic movement in figure drawing. Since muscle shapes change with angles and motion, careful observation and anatomical awareness are key.
Understanding Muscle Function and Form
Before diving into sketching, it’s essential to understand how muscles behave. Muscles stretch, bend, and contract in response to the body’s movement. Each muscle group has a specific role depending on its location. A foundational knowledge of muscle anatomy will help you draw with both accuracy and artistic flair.
How to Draw Muscles of the Torso
Back and Shoulder Muscles
Start with the trapezius, the large muscle on the upper back that connects the neck to the shoulders and helps in scapula movement. From a front view, the trapezius outlines the area between the neck and clavicles, forming triangular shapes that guide your sketch.

Next, note the latissimus dorsi, or dorsal muscle, which is broad and flat, extending from the middle back to below the armpits. It enables arm extension and connects to the humerus bone.
Chest and Ribcage Muscles
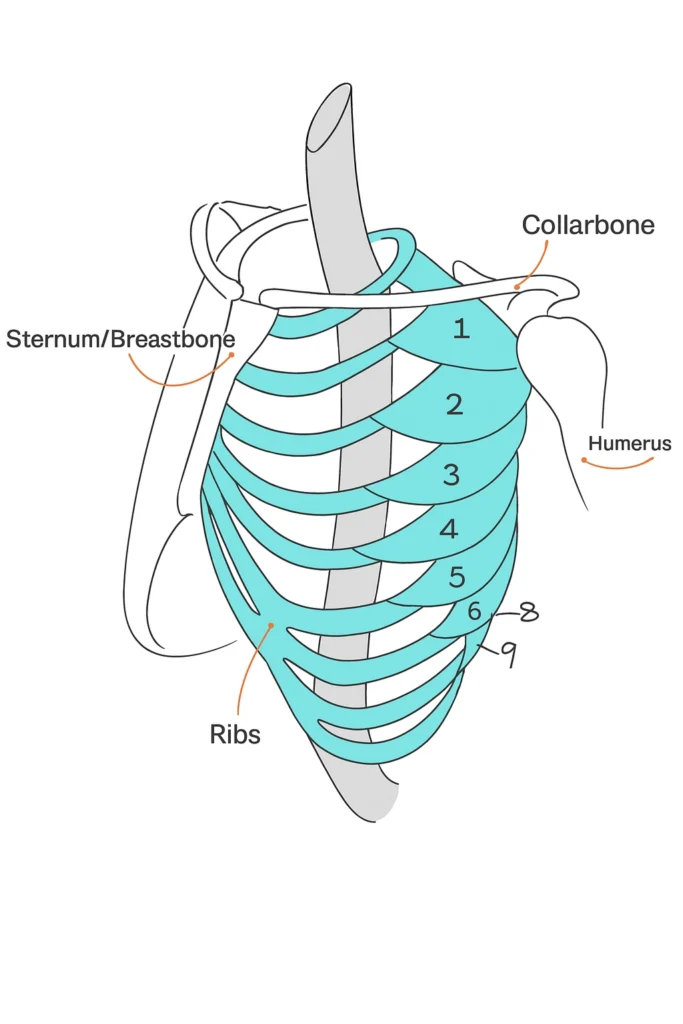
The serratus anterior fans out from the scapula to the upper nine ribs, often visible under the arms. It provides structure and mobility, overlapping the obliques, dorsals, and pectorals. Meanwhile, the pectoral muscles attach to the humerus and stretch across the chest, allowing arm rotation. Remember that in female anatomy, the breasts sit on top of the pectorals and begin from the middle, not the collarbone.
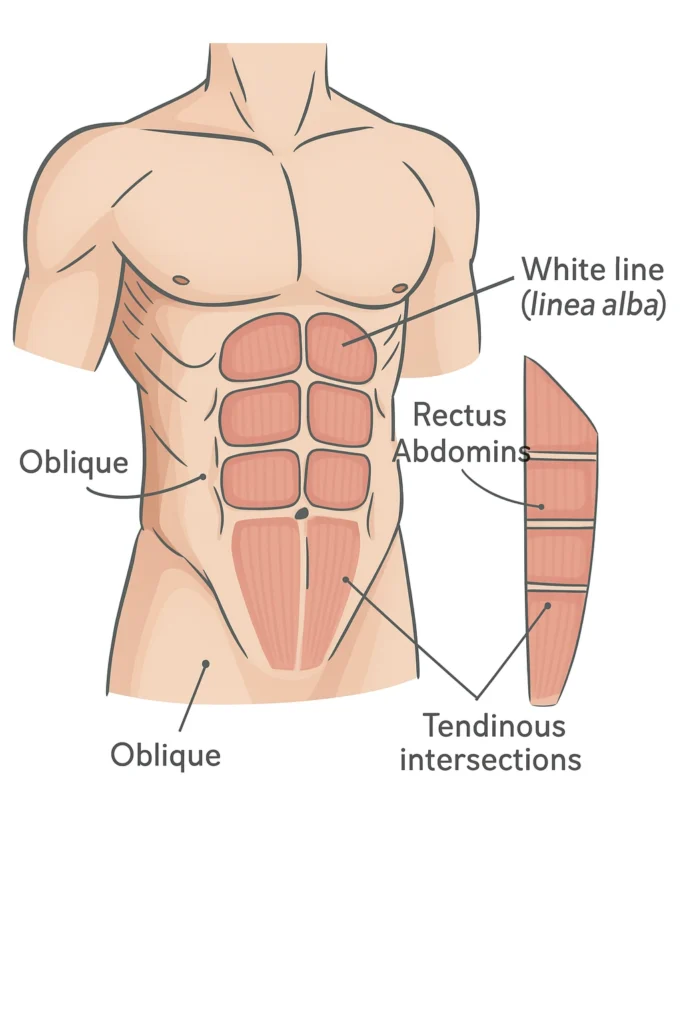
Abdominal Muscles
The rectus abdominis muscle runs vertically from below the ribs to the pubic area and is split by the linea alba into left and right sides. Horizontal intersections divide it into four parts, commonly referred to as “abs.” On the sides, the obliques are visible above the hip bones and contribute to twisting, bending, and rotating the torso. When viewed from the side, muscles may appear interlocked in a zig-zag pattern, which is important to observe for realistic rendering.
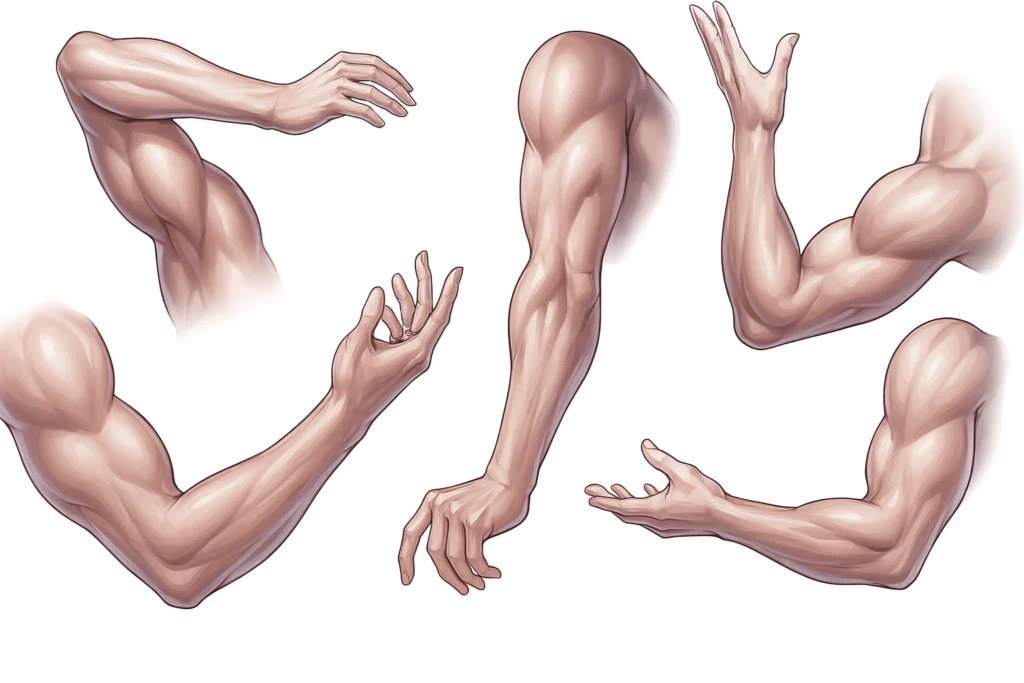
How to Draw Muscles of the Arms and Legs
Upper Arm Muscles
The deltoid muscle, thick and triangular, wraps around the shoulder. It originates from the collarbone and inserts into the upper arm bone (humerus). Just beneath it lies the brachialis, which acts as a separator between the biceps (oval-shaped) and the triceps (with a horseshoe shape when flexed).

Forearm and Hand Muscles
Muscles in the forearm are elongated, thin, and slightly flat. They control hand and finger movement. Due to their similarity in shape, careful observation is crucial before drawing to prevent confusion and ensure anatomical accuracy.
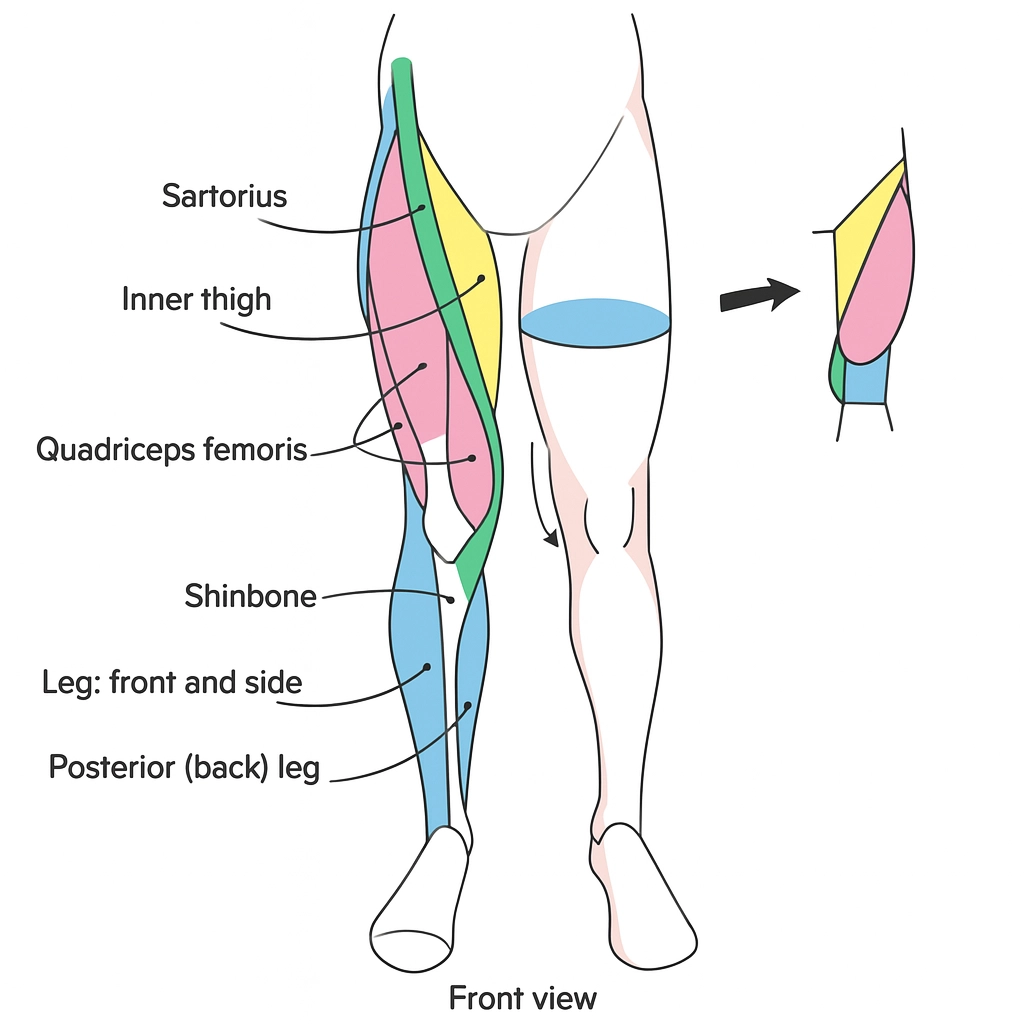
Leg Muscles Overview
Though this guide focuses more on the upper body, apply similar principles when drawing leg muscles. Note how the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles function and observe their shifting shapes in relation to posture and movement.
Final Tips on How to Draw Muscles Precisely
There are many ways to approach drawing muscles, but the key lies in observation. Whether you follow anatomical references, sketch from life, or study 3D models, your precision depends on how attentively you interpret form, proportion, and expression. Remember, your goal isn’t just to replicate muscle shapes but to integrate them into a living, moving figure. By understanding how to draw muscles, you bring your characters to life—imbuing them with energy, strength, and realism.




